Struggling with air leaks or jerky motion in your pneumatic cylinder? The wrong seal could be the root cause—costing you time, efficiency, and money.
To properly seal a pneumatic cylinder, you need to match seal types and materials to your operating conditions—pressure, speed, temperature, and contamination. This guide will show you exactly how to do that.

Choosing the correct pneumatic seal is easier than you think. Let’s break it down by function, material, and usage so you can make informed, confident decisions.
What factors should I consider when choosing pneumatic cylinder seals?
You might feel overwhelmed with options—but choosing the right seal starts with asking the right questions.
Select seals based on pressure level, operational speed, media exposure, and temperature range. For example, low-friction seals suit high-speed tasks, while heat-resistant FKM seals perform well under thermal stress.

What parameters matter most when selecting pneumatic cylinder seals?
| Criteria | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Pressure | Up to 10 bar → Use NBR, TPU, FKM |
| Speed | High-speed → Choose low-friction piston seals |
| Temperature | FKM for high heat, NBR for standard use |
| Environment | Dusty areas → Add dust wiper seals |
| Motion Energy | Use buffer seals |
| Supplier | Choose from trusted pneumatic seal suppliers |
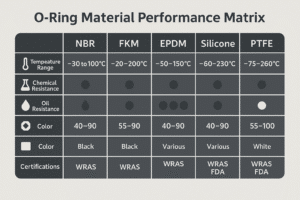
What materials are best for pneumatic seals?
Choosing the wrong seal material will lead to premature failure—but how do you know which is best?
NBR is cost-effective for standard air cylinders, FKM resists heat and chemicals, and TPU is ideal for wear-prone environments. Always match materials to your specific conditions.

Which seal materials suit specific environments?
| Material | Key Features | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| NBR | Economical, oil-resistant | General pneumatic cylinders |
| FKM | Heat & chemical resistant | Food, pharma, hot zones |
| TPU | Tough, abrasion-resistant | Fast-cycle, dusty areas |
What are common signs of pneumatic seal failure?
Frequent breakdowns or slow response? Your seals may be worn.
Watch for symptoms like air leaks, inconsistent movement, or oil mist. These signal seal degradation and a need for immediate inspection.

How do you diagnose a worn pneumatic seal?
- Sluggish cylinder response
- Air hissing or pressure drop
- Visible wear on rods
- Increase in service intervals
Can I use hydraulic seals in pneumatic cylinders?
It’s tempting to substitute seals, but it’s not worth the risk.
Hydraulic seals have tighter tolerances and stiffer materials. These increase friction and reduce performance in air systems. Use seals made specifically for pneumatics.
How often should I replace pneumatic cylinder seals?
Even the best seals wear out—but proactive replacement can prevent breakdowns.
Most seals last 6–24 months. High-speed and dusty environments shorten their life. Replace dust seals more frequently to block contaminants.
What’s the recommended seal replacement schedule?
| Seal Type | Typical Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Rod Seals | 12–18 months |
| Piston Seals | 18–24 months |
| Dust Wipers | 6–12 months |
| Buffer Seals | Replace when impact softens |
Conclusion
The right seal boosts efficiency, minimizes downtime, and extends your cylinder's life. Choose wisely based on environment and motion needs.
Choose the right seal today
Need help identifying or customizing pneumatic seals?
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 17622979498
Let us help match your specs with no MOQ required.
Related topic
How Do Pneumatic Cylinder Seals Work?
Types of Pneumatic Cylinder Seals
Pneumatic vs Hydraulic Seals