Facing air leaks, reduced efficiency, or damaged components in your pneumatic systems? You're not alone. Choosing the right pneumatic cylinder seals can make or break your operation’s reliability and lifespan.
Pneumatic cylinder seals prevent air leakage and contamination by sealing gaps between pistons, rods, and end caps. Their proper function ensures efficient pressure retention, smooth motion, and longer equipment lifespan.

Understanding each type of pneumatic seal and how it functions can save your system from premature wear. Let's dive into what matters most when choosing the right seal.
What types of pneumatic seals are used in cylinders?
Confused by terms like piston seals, rod seals, or wipers? You're not alone. Many struggle to pick the right type for their application.
Pneumatic cylinders use piston seals, rod seals, dust wiper seals, and buffer seals. Each plays a specific role in sealing air, reducing friction, and protecting system components.
What does each pneumatic seal type do?
| Seal Type | Function | Common Materials | Product Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piston Seals | Seal internal pressure on piston head | NBR / FKM / TPU | Pneumatic Cylinder Seals |
| Rod Seals | Seal air around moving rod | NBR / FKM / TPU | Rod Seals |
| Dust Wiper Seals | Prevent dirt ingress | TPU / NBR | Dust Wiper Seals |
| Cushion Seals | Absorb motion energy | TPU / Rubber blends | Buffer Seals & Cushion Rings |
How do pneumatic piston seals maintain motion and pressure?
Ever wonder what keeps air inside a moving pneumatic cylinder? It’s all about the piston seal.
Pneumatic piston seals trap compressed air between the piston and cylinder wall. This force moves the load. A leak here ruins actuation.
What happens inside a pneumatic cylinder?
In a bottling plant I visited, inefficient seals caused pressure loss in air-operated presses. After installing high-grade pneumatic piston seals, efficiency improved by 23% and downtime dropped.
Step-by-Step Process:
- Compressed air enters the cylinder.
- Piston seal traps air ahead of the piston.
- Air pressure pushes piston forward.
- Seal blocks reverse airflow.
- Air exhausts post-stroke.
How do I select the right pneumatic cylinder seal?
Choosing a seal isn’t just about diameter—it’s about durability.
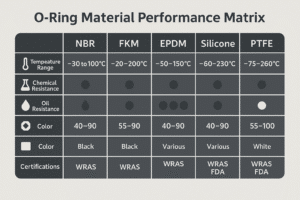
To pick correctly, match operating pressure, stroke type (rotary or linear), environment (dust, heat), and air composition. Then choose seal materials: NBR (economical), FKM (high heat), TPU (abrasion-resistant).
What should I consider when choosing a seal?
| Application Factor | Recommended Seal Type |
|---|---|
| High temp zones | FKM or PTFE-based seals |
| Long cycle life | TPU with low-friction profiles |
| Dusty setups | Dust Wiper Seals essential |
| Heavy loads | Cushion Seals to absorb energy |
| Precise motion | Tight-tolerance O-rings, often custom fit |
What’s the difference between pneumatic and hydraulic seals?
Hydraulic and pneumatic seals might look similar—but their performance profiles differ.
Pneumatic seals handle high-speed, low-pressure air. Hydraulic seals work under slow, high-pressure oil flow. Using one in place of the other causes leaks, wear, or failure.
Pneumatic vs Hydraulic Comparison
| Property | Pneumatic Seals | Hydraulic Seals |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Range | Up to 10 bar | Up to 400 bar |
| Working Fluid | Compressed air | Hydraulic oils |
| Material Type | NBR, FKM, TPU | PU, PTFE, NBR |
| Primary Concern | Friction, speed, contamination | Pressure retention, durability |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Conclusion
Pneumatic cylinder seals are your first line of defense against air leaks. Knowing each seal's role and material improves system reliability, reduces cost, and boosts productivity.
Need help picking the right pneumatic seal?
We match seals to your size, specs, or application:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 17622979498
Get expert support, fast shipping, and no MOQ.
Related topic
Pneumatic Cylinder Seals: What Are the Top Benefits in 2025?
5 Common Problems with Pneumatic Cylinder Seals & How to Fix Them
How to Extend the Lifespan of Your Pneumatic Cylinder Seals?