When I first dealt with leaking pneumatic systems, I realized that reliable sellos de cilindros neumáticos aren’t optional — they’re essential.
These small components prevent air loss, increase efficiency, and keep your operations running smoothly. So, how do they actually work, and which ones should you use?

Let’s explore the function, types, replacement tips, and top options in 2025.
What is the function of a pneumatic cylinder seal?
Pneumatic cylinder seals create airtight barriers inside cylinders to control compressed air.
They stop leaks, reduce wear, and improve pneumatic efficiency — without them, cylinders lose pressure and energy fast.

| Función | Result |
|---|---|
| Sealing air gaps | Prevents energy loss from leaks |
| Reducción de fricción | Smooths piston/rod movement |
| Pressure retention | Maintains stroke power and directionality |
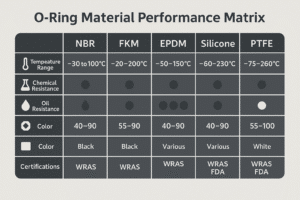
Most seals are made of NBR, PTFE, or TPU — each with unique strengths.
How do pneumatic cylinder seals work?
They act like airlocks inside cylinders.
- Sellos de varilla stop leakage along the piston rod
- Sellos de pistón keep pressure inside the cylinder
- Wiper seals block contaminants like dust and grit

| Tipo de sello | Ubicación | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Sello de varilla | Rod passage | Prevents external air loss |
| Sello de pistón | Inside chamber | Maintains pressure for stroke motion |
| Sello del limpiaparabrisas | Outer entry point | Keeps debris out of cylinder internals |
You’ll often find all three in a seal kit by size.
What’s the difference between single-acting and double-acting seals?
The direction of air pressure defines the seal type.
De simple efecto cylinders move in one direction and reset via spring or load.
Doble efecto ones use air for both directions — needing more robust seals.

| Tipo | Air Movement | Caso de uso |
|---|---|---|
| De simple efecto | De una sola mano | Low-load automation or clamping tasks |
| Doble efecto | De dos vías | Precise movement, industrial robotics |
Double-acting seals often require KDAS compact seal designs.
How often should you replace pneumatic cylinder seals?
Generally, check every 6–12 months. But in my experience, visual cues matter most.
Watch for:
- Air leaks
- Slow motion or sticking
- Surface cracks or flattened edges
| Condición | Action |
|---|---|
| Air loss | Reemplazar inmediatamente |
| Aumento de la fricción | Clean, then reassess fitment |
| Cracking | Change the seal before failure |
I always keep a spare seal kit ready on-site — it’s saved me multiple breakdowns.
How do I choose the right seal for my system?
Three things matter most: material, pressure rating, y chemical compatibility.
| Factor | Recomendación |
|---|---|
| Material | Use NBR for oil, PTFE for low friction, TPU for shock loads |
| Operating pressure | Choose reinforced seals for high PSI |
| Environmental fit | Opt for weather-resistant TPU or FKM |
Need something non-standard? Use Hengoseal’s custom seal service.
Which industries use pneumatic cylinder seals most?
You’ll find these seals in almost every automated system.
| Industria | Application Example |
|---|---|
| Automatización | Cylinder actuation in packaging lines |
| Procesamiento de alimentos | Clean-motion controls with TPU seals |
| Automotor | Pneumatic arms and lift systems |
| Robótica | Compact linear motion with zero leakage |
My client in the food sector switched to FDA-grade wiper seals — hygiene issues dropped, and downtime vanished.
Conclusión
Pneumatic cylinder seals are the backbone of pressure-controlled movement.
Get the right one, and you’ll enjoy leak-free performance, longer service life, and optimized motion in every stroke.
Talk to us about your cylinder seal application
📩 邮箱:[email protected]
📞 WhatsApp:+86 17622979498
Related post
- 2025 Pneumatic Cylinder Seal Guide
- Best Material for Pneumatic Cylinder Seals
- Seal Failures and Fixes
- Piston Seal Types & Applications
- Seal Lifespan Extension Tips