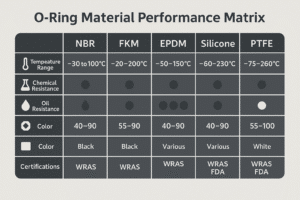
Choosing the wrong seal material in a chemical plant can lead to catastrophic leaks, equipment corrosion, and expensive downtime. PTFE and FKM are top contenders — but which one truly holds up under harsh chemicals?
PTFE offers superior chemical resistance, while FKM brings elasticity and heat tolerance. Yet in chemical plant environments, the "best" option depends on your media, pressure, and system design. Let’s break it down.

When engineers fail to match seals to specific chemicals, premature failure is almost guaranteed. This guide compares PTFE and FKM across five real-world criteria so you can make the right choice for long-term reliability.
What are the key differences between PTFE and FKM seals?
| Proprieto | PTFE | FKM (Viton®) |
|---|---|---|
| Kemia rezisto | Resistant to 99% of chemicals | Resistant to most oils, acids |
| Temperaturintervalo | -200 °C ĝis +260 °C | -30°C to +230°C |
| Elasteco | Rigid, low rebound | Flexible, elastic |
| Compression set | Alta | Malalta |
| FDA / EU compliance | Yes (pure PTFE) | Yes (limited compounds) |
PTFE performs better in static chemical sealing, especially in systems exposed to harsh acids, alkalis, and solvents. FKM seals, like our FKM O-Rings for high-temperature sealing, are better for dinamika sigelo where flex and compression are critical.
Which chemicals degrade FKM but not PTFE?
FKM fails in highly polar solvents and strong bases like:
- Acetono
- Amoniako
- Sodium hydroxide
- Ketones (MEK, MIBK)
PTFE, being non-polar and inert, resists all of the above without swelling, making it ideal for:
- Chlor-alkali plants
- Paint production
- Acid-processing lines
Our clients in chemical transfer pump systems use PTFE O-Ring Kits for long-term sealing where acid concentration exceeds 80%.
Is PTFE suitable for dynamic sealing in chemical pumps?
Only in certain cases. While PTFE offers unbeatable chemical resistance, it lacks elasticity — leading to poor recovery and higher torque requirements in dynamic environments.
For sliding or rotating seals, FKM is more reliable due to its lower friction and better shape memory. That’s why chemical pump OEMs often combine PTFE static seals + FKM dynamic seals in one assembly.
For example, our dual-material sealing kits using FKM energizers with PTFE jackets have shown 3x lifespan improvement in batch chemical reactors.
Which seal material lasts longer in heat and chemical exposure?
PTFE lasts longer when exposed to:
- High temperature + strong acid
- Fluctuating chemical mixtures
- Long-term immersion
However, it’s prone to creep and mechanical wear under compression. FKM maintains shape better but may degrade faster under prolonged acid exposure at high temps.
Case study: In a sulfuric acid filling line (70°C), standard FKM lasted 4 weeks. After switching to PTFE rotary shaft seals, seal change intervals extended to 6 months.
How to choose between PTFE and FKM based on your chemical application?
Here’s a quick reference:
| Media Type | Best Seal Material |
|---|---|
| Strong acids | PTFE |
| Ketones & esters | PTFE |
| Oils & fuels | FKM |
| Vaporo | FKM aŭ PTFE |
| Caustic soda | PTFE |
| Mixed chemicals | PTFE (preferred) |
For mixed-media sealing, we recommend using custom-designed seal stacks that layer PTFE and FKM to balance resistance and elasticity.
Konkludo
If your sealing environment involves aggressive chemicals or high temperatures, PTFE is the safer long-term choice. But in dynamic sealing or high-pressure systems, FKM might offer better resilience and performance.
Related topic
PTFE O Ring Kit: Best for Heat & Chemicals
FKM Seal Selection Guide for Harsh Media
O-Ring Seal Basics: How They Work & Where to Use
Need help picking the right material?
Chemical plants need seals that work first time, every time. Let Hengoseal help you choose PTFE or FKM based on your process media.
📧 Retpoŝto: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 17622979498
Get a custom recommendation in 24 hours.