Frequent leaks, pressure drops, or erratic movements in your pneumatic systems? It's often the seals. Optimizing material selection and maintenance can double seal lifespan, slashing downtime and costs.
Pneumatic seals fail mainly due to friction, contamination, and improper material choice. This guide shows you how to prevent failures, extend service life, and maintain top equipment performance.

Want your equipment running longer and smoother? Let’s dive into practical solutions for maximizing seal lifespan.
Why Do Pneumatic Seals Fail in Industrial Equipment?
Why do seals wear out faster in industrial settings?
- Excessive friction from poor lubrication.
- Dirt and debris contamination.
- Incorrect material for pressure, chemicals, or heat.
- Overpressure or extreme temperatures.
- Improper installation causing misalignment.
👉 Prevention starts with correct materials, installation, and maintenance.

Selecting seals that match your equipment’s conditions—like PTFE for aggressive chemicals—is key to longevity.
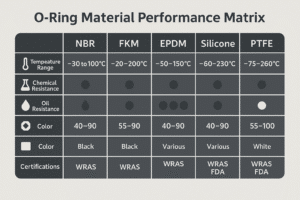
How to Choose the Right Material for Pneumatic Seals?
What material offers the best durability for pneumatic seals?
| Material | Temp Range | Pressure | Best For | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR | -30°C to 110°C | Low-Med | General use | Oil-resistant, budget-friendly |
| TPU | -40°C to 100°C | High | Heavy-duty systems | Superior wear resistance |
| FKM | -20°C to 200°C | Med-High | Chemicals & heat | High durability |
| PTFE | -200°C to 260°C | High | Extreme conditions | Chemically inert |
| Silicone | -60°C to 230°C | Low | Food/medical | Flexible, non-toxic |
🔎 Need maximum lifespan? TPU & PTFE are top choices for industrial durability.
See HENGOSEAL's pneumatic seal range.
What Maintenance Practices Extend Pneumatic Seal Lifespan?
Which practices are essential for seal longevity?
- Proper Lubrication: Use silicone or PTFE-based lubricants.
- Cleanliness: Install air filters to block contaminants.
- Pressure Control: Operate within seal-rated limits.
- Routine Inspections: Replace worn seals early.
- Correct Installation: Use tools & lubrication to avoid damage.
💡 Tip: For dusty environments, reinforce with wiper seals.
How to Detect Early Pneumatic Seal Failure?
Look for these warning signs:
- Hissing air leaks.
- Jerky actuator movements.
- Excess friction & heat buildup.
- Visible cracks or hardened seals.
- Dust or oil residue near seals.
Timely detection prevents expensive failures. Regular checks are a must.
Common Mistakes That Shorten Seal Life
What mistakes reduce pneumatic seal performance?
- Wrong lubricants degrading rubber.
- Skipping regular inspections.
- Incorrect installation techniques.
- Using unsuitable materials for the environment.
✅ Fixing these errors significantly boosts seal lifespan.
Why Choose HENGOSEAL Pneumatic Seals?
Why is HENGOSEAL trusted by global industries?
- Premium TPU, PTFE, NBR, FKM materials.
- Designed for wear, heat & chemical resistance.
- Custom sizes & OEM solutions.
- Fast global delivery, no MOQ limits.
📩 Get a quote: [email protected] | 📱 WhatsApp: +86 17622979498
🌐 Browse our pneumatic seal catalog.
Conclusion
Extend pneumatic seal life by choosing the right materials, ensuring clean operation, and maintaining correct pressure & lubrication. Smart maintenance cuts costs and boosts equipment reliability.
Upgrade Your Pneumatic Seals Today
📩 [email protected] | 📱 WhatsApp: +86 17622979498
Related topic
High-Performance Pneumatic Seals for Industrial Applications
Best Practices for Extending Pneumatic Seal Lifespan
Top Causes of Seal Failure & How to Prevent Them