Imagine your production line grinding to a halt because of a tiny air leak. Sounds frustrating, right? That’s exactly why pneumatic seals are essential—they keep compressed air contained, ensuring your machines run efficiently, quietly, and without interruption.
Whether you're in automation, food processing, or medical production, understanding how pneumatic seals work can prevent costly downtime.
What Are Pneumatic Seals and Why Are They So Important?
Pneumatic seals are components used to contain pressurized air in machinery systems. Their primary job is to prevent leakage between moving and stationary parts while allowing smooth mechanical motion.
Without proper pneumatic sealing, you risk air loss, erratic equipment behavior, and energy inefficiency.
Key benefits of pneumatic seals include:
- Maintaining stable air pressure
- Reducing energy consumption
- Extending equipment life
👉 Need OEM-ready pneumatic cylinder seals? Check out our complete pneumatic cylinder seals collection.
How Do Pneumatic Seals Work?
Pneumatic seals sit between moving parts—like pistons and rods—and form a tight barrier that keeps compressed air from leaking out.
| Feature | Role in System |
|---|---|
| Air Tightness | Maintains system pressure |
| Low Friction | Supports dynamic movement |
| High Durability | Resists wear from constant cycling |
What Are the Different Types of Pneumatic Seals?
Pneumatic systems use several types of seals. Each serves a specific role in preventing leaks and keeping components aligned.
Common Pneumatic Seal Types
| Seal Type | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Piston Seals | Prevent air leakage inside the cylinder |
| Rod Seals | Seal the system where the rod exits the cylinder |
| Wiper Seals | Block contaminants from entering the system |
| Wear Rings | Guide the piston and prevent metal contact |
Looking for OEM packaging and flexible MOQ? Visit our pneumatic cylinder seal supplier page.
Where Are Pneumatic Seals Used?
Pneumatic seals are found across industries where air pressure powers motion:
- Manufacturing Automation
- Automotive Assembly
- Food & Beverage Machinery
- Medical Equipment
They are essential in precision systems where clean and fast movement matters.
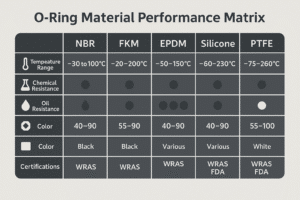
What Materials Are Used for Pneumatic Seals?
Material choice affects resistance to temperature, friction, and chemicals. Here’s a breakdown of the most common materials:
| Material | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| NBR (Nitrile) | Affordable, flexible, oil-resistant |
| PTFE (Teflon) | Low friction, chemical resistance, rigid |
| FKM (Viton®) | High-temp and chemical stability |
| Polyurethane (PU) | High wear resistance and elasticity |
Browse all material options in our pneumatic seals product catalog.
Can Pneumatic Seals Handle Pressure Like Hydraulic Seals?
No. Pneumatic seals are designed for low-pressure systems (6–10 bar), while hydraulic seals manage much higher pressures (up to 400 bar).
| Factor | Pneumatic Seals | Hydraulic Seals |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Air | Oil/fluid |
| Pressure Range | Low (6–10 bar) | High (100–400 bar) |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Seal Material | Softer and more flexible | Tougher, oil-resistant |
Want more insight? See our guide: Hydraulic vs. Pneumatic Seals
What Are the Signs of Pneumatic Seal Failure?
- Air leaks
- Loss of pressure
- Irregular motion
- External contamination on rods
Regular inspection helps avoid these common failures. Read more on common pneumatic seal issues.
How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Seal?
Choosing the wrong seal can cost you time and money. Here's what to evaluate:
- Pressure & Temperature — Match materials to your system's limits.
- Seal Type — Identify piston, rod, or wiper needs.
- Material Resistance — Consider oil, chemicals, and friction.
- Seal Lifespan — Aim for durable, long-wearing options.
Need help choosing? We support low MOQ and OEM packaging for all types.
👉 Check size charts and lead times here.
What Are the Best Pneumatic Seal Materials for Industrial Use?
If your application involves:
- Frequent motion → Choose PU
- High temperatures → Go with FKM
- Chemical resistance → Opt for PTFE
Explore options in our pneumatic seal range
Final Thoughts: Why Sealing Right Matters
Pneumatic seals may be small, but they’re a big deal in keeping your operations smooth. With the right material and design, you reduce air leaks, increase uptime, and extend equipment life.
→ Get a quote or explore product details